Driver for Green Antenna Innovation
Climate change is an urgent global crisis, and limiting global warming to 1.5°C is essential to avoid catastrophic consequences. To achieve this ambitious goal, we must transition to a green economy. The ICT industry, particularly wireless networks, plays a crucial role in this transformation.
Antennas, as fundamental components of wireless networks, offer a significant opportunity to reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions. By innovating antenna technologies, we can optimize network performance while minimizing environmental impact. This white paper explores the key areas of technological advancement for base station antennas to drive sustainable wireless networks.
To ensure optimal signal transmission and reception, antennas are typically installed at elevated positions like towers and rooftops, minimizing obstructions. Visually, these base station antennas are often seen piercing the sky. Inspired by this image, we’ve titled this white paper “The Green Antenna Innovation White Paper.”

Table of Contents
Energy Saving
Considering the specific characteristics and diverse applications of antennas, this white paper explores three key areas of green innovation: energy efficiency, sustainable deployment, and eco-friendly manufacturing.
Considering the specific characteristics and diverse applications of antennas, this white paper explores three key areas of green innovation: energy efficiency, sustainable deployment, and eco-friendly manufacturing.
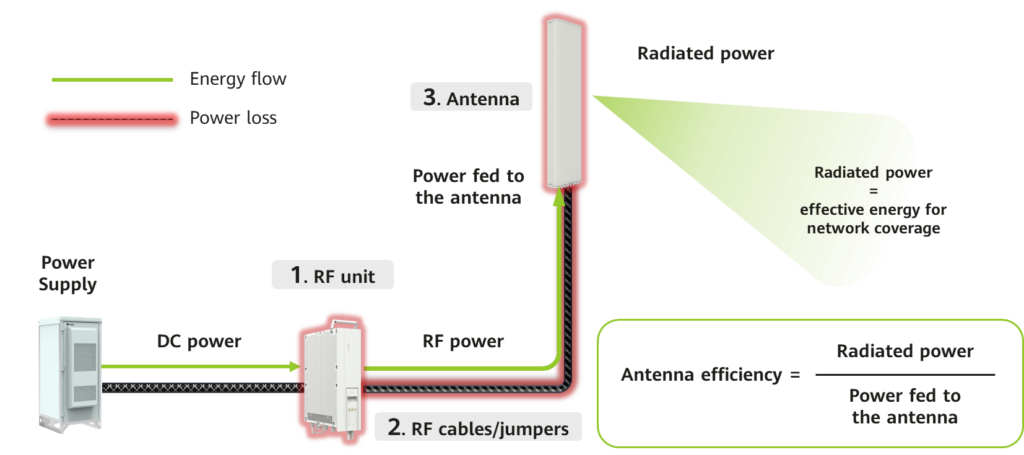
As depicted in the figure, an RF unit supplies RF energy to an antenna through RF cables (feeders or jumpers), and the antenna subsequently radiates this energy as electromagnetic waves. However, in reality, antennas cannot convert all the input RF energy into radiated electromagnetic waves. Some energy is inevitably lost due to factors like return loss, insertion loss, and other inefficiencies. To quantify this conversion performance, antenna energy efficiency is defined as the ratio of the radiated electromagnetic wave energy to the input RF energy.
Antenna efficiency =
Power radiated by the antenna/Power fed to the antenna
Moreover, it’s crucial to account for energy loss within the cable connecting the RF unit and the antenna. The extent of this loss is influenced by factors such as cable type and length. In certain scenarios, energy loss can be substantial, reaching up to several tens of percentage points.
The antenna-radiated energy is the effective portion that can be used for mobile communication. As depicted above, a higher antenna energy efficiency and a smaller cable loss means that the RF device can feed less RF energy for the same coverage performance. This offers a way to reduce base station energy consumption by lowering the output power of the RF devices. Therefore, increasing antenna energy efficiency and reducing cable loss are effective and essential to reduce the energy consumption of base stations, and are the primary tasks of antennas’ green innovations
Green Deployment
The primary challenges associated with antenna deployment can be summarized as follows:
Technical Challenges
- Height Requirements: To ensure optimal network coverage, antennas often need to be installed at significant heights. This poses technical challenges related to signal propagation and interference.
- Size and Weight: Antennas, especially those for advanced technologies like 5G, can be bulky and heavy. This complicates installation and maintenance processes.
Logistical Challenges
- Site Infrastructure: The installation site must have sufficient load-bearing capacity to support the weight of the antenna and withstand potential wind loads.
- Installation Process: The deployment process often involves delicate high-altitude operations, requiring specialized equipment and trained personnel.
- Environmental Impact: Antennas, particularly those on rooftops or towers, can be visually intrusive. There are often strict regulations and community concerns to address regarding their aesthetic impact
Resource Consumption
- Cost: The specialized equipment, skilled labor, and site preparation required for antenna deployment can be costly.
- Time: The complex installation process can be time-consuming, delaying network rollout.
- Energy: Antennas consume energy for their operation and cooling. This can contribute to increased energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Analyzing the Impact of Antenna Replacements on Network Evolution
Key Challenges Arising from Frequent Antenna Replacements:
- Resource Consumption:
- Site Acquisition and Preparation: Each new antenna installation requires site acquisition, permits, and infrastructure development, leading to significant resource consumption.
- Construction and Installation: The physical installation of antennas, including tower construction, cabling, and power supply, involves substantial costs and environmental impact.
- Equipment and Labor: The procurement and deployment of new antennas require significant investments in equipment and skilled labor.
- Operational Efficiency:
- Network Outages: Antenna replacements can disrupt network services, leading to potential revenue loss and customer dissatisfaction.
- Maintenance Costs: Frequent replacements increase maintenance costs, including labor, spare parts, and logistics.
- Environmental Impact:
- Material Waste: Discarded antennas and packaging contribute to electronic waste.
- Energy Consumption: The production and transportation of new antennas consume energy and generate greenhouse gas emissions
The Importance of Green Deployment:
Green deployment of antennas focuses on minimizing resource consumption and environmental impact throughout the antenna’s lifecycle. Key strategies include:
- Modular Design: Modular antennas can be easily upgraded or replaced, reducing the need for complete antenna replacements.
- Longer Lifespan: Designing antennas with robust materials and advanced cooling systems can extend their operational life.
- Efficient Installation: Streamlined installation processes, such as pre-assembled antenna modules, can reduce deployment time and costs.
- Energy-Efficient Antennas: Utilizing energy-efficient technologies, such as power-saving modes and efficient cooling systems, can reduce energy consumption.
- Sustainable Materials: Employing eco-friendly materials in antenna construction can minimize environmental impact.
- Recycling and Reuse: Implementing effective recycling programs for end-of-life antennas can reduce waste and conserve resources.By adopting green deployment principles, network operators can achieve more sustainable and efficient network evolution, while also contributing to environmental conservation.






